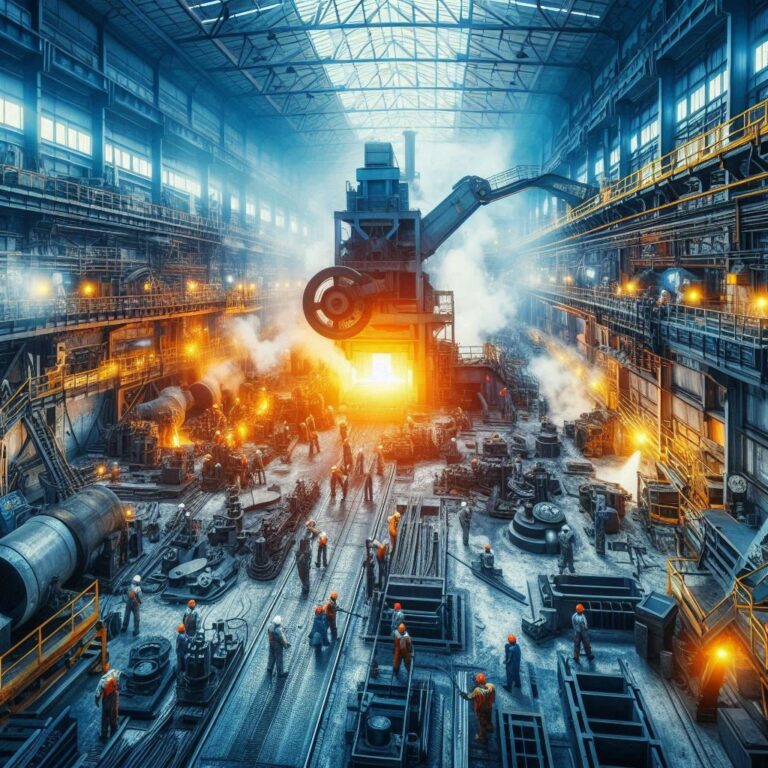
Choosing a dependable industrial partner amid the Indian foundry sector’s expansion demands turning procurement into a technical audit instead of just a transactional one. A significant resistance when purchasing from Sand Casting Manufacturers India is not that capacity is readily available—after all, India ranks as the world’s second-largest producer of castings—but rather that process discipline is consistent.
Here we dive deep into several sand casting process intricacies which will eventually lead procurement executives and engineers beyond just price checks and certifications to evaluating Indian manufacturers.
Managing sand casting processes carefully
Pouring liquid metal into a hollow made of sand creates objects through sand casting. One-time molds using basic raw ingredients mean results can differ each time. In places like India, shifting weather – lots of moisture, heat swings – demands careful handling to avoid issues during production
In the first place, buyers both local and global must locate a Sand Casting Manufacturer India who have institutionalized their processes. The term ‘tribal knowledge’ is used to describe the situation in which the quality depends on a specific skilled worker, and such a matter finding the definition of the problem is a prerequisite to shifting from this system to precision (quality being the outcome that emanates consistently from the machinery and the protocols put in place).
Sand Preparation and Property Management
Sand casting being the most important process variable, hence it must have the combined qualities of strength to hold its form, sufficient permeability for gases to escape, and chemical inertness to prevent reaction with molten metal.
Green Sand Systems
Lots of Sand Casting Manufacturers India at high volume production scale uses Green Sand which is a mixture of silica sand, bentonite clay, water, and coal dust. Green refers to the water presence. Definite control of following properties implemented:
- Water Content: This aspect must be controlled within very narrow limits (normally 3%-5%). Excess of water generates steam which ultimately causes gas defects.
- Green Compression Strength (GCS): This parameter determines how well the mold can hold the molten metal pressure. A low GCS can result in mold swelling or breaking.
- Compactibility: This is maybe the foremost indication of how well the sand behaves when undergoing mechanical pressure from an automated molding. The best foundries have online sand mixers that control water and clay addition by real-time sensor data.
No-Bake (Chemically Bonded) Systems
For a bigger and intricate casting, the No-Bake process is the possible choice. Here, sand is mixed with resin and a catalyst. Controls are laid on:
- How Constant is the Reclamation: High-grade makers use mechanical or thermal sand reclamation methods, but they have to strictly monitor loss-on-ignition (LOI) so as not to undermine the density of newly made molds with leftover chemicals.
- How Sensitive Are You to Temperature: Resin setting time varies greatly with temperature. Industrial conglomerates in India now temper sand fired bricks or alter catalyst ratios on an hourly basis to cope with an everchanging environment.
Pattern Engineering and Tooling Standards
The pattern sets the limit on casting quality. Usually, a mistake when one is sourcing from the India market is being cheap on tooling.
Material Selection
Fewer coins leave your pocket with wooden molds – yet monsoon dampness often twists them out of shape. Experts at Indian sand casting firms still demand:
- From cars to heavy manufacturing, aluminum or cast iron molds hold shape under repeated use. What matters most? Consistent measurements every single time. Machines keep building parts exactly alike, thanks to these sturdy metal forms. Precision stays locked in, cycle after cycle. Stability comes from material toughness, nothing else.
- Heavy plastics or resins work well when making a moderate number of items. They hold up against dampness more than wood does.
Design for Manufacturability (DfM)
A factory’s design and engineering department shall give feedback on draught angles (facilitating smooth withdrawal of the pattern) and fillet radii (avoiding stress concentration and “hot tears” lead). In case a vendor just simply accepts a drawing without raising a question about the feasibility of the casting, this frequently signals that they are not technically deep.
Advanced Metallurgy and Melt Control
Upgrading recycled materials to add new alloying elements in a controlled atmosphere is the hallmark of most sophisticated Sand Casting Manufacturers India.
Spectrometric Analysis
At the melting point, the chemical make-up ought to comply with the specified ranges for carbon, silicon, manganese, phosphorus, sulfur, and other alloying elements from chromium, nickel, chromium, nickel, etc.). Storing ensures that chemical composition is within proper limits by analyzing a thin slice of metal called a sample.
- Actionable Advice: Procurement Head should request “Heat-wise Spectro Reports.” The ones from a trustworthy vendor are digitized and traceable to each batch shipped.
Inoculation and Spheroidization
Magnesium treatment of cast iron, also called ductile iron, is a thing several Indian foundries try to control strictly. The fade time here refers to the time duration before magnesium loses its effectiveness and must therefore be tightly controlled.
- Nodularity Checks: This involves an instant microscopic inspection to verify that the graphite in the iron is of the spherical shape and not flake.
- Pouring Temperature: (Monitoring utilizing infrared pyrometers).
Gating, Risering, and Simulation Technology
One of the biggest changes that the best Indian manufacturers of sand castings have undergone is to abandon the technique of trial and error for gating design for the methoding simulation.
What Simulation Brings
Engineers using software such as Magmasoft or Pro CAST can determine on the computer, where the molten metal will stay longest and where it is most turbulent. At the same time, they can also work on optimizing the utilization of the metal in the process of solidification that is still under the metal as well as the final product and the process develop.
- Hot Spots: Areas in the casting that stay molten longer and more prone to shrinkage cavities.
- Turbulence: Spots where the metal break is turbulent, which can entrap air or wash away sand.
- Yield optimization: Striking the right balance between the need for “risers” (metal reservoirs) and the need for cost-efficiency.”
Critical Takeaway: When evaluating suppliers, examine their simulation reports on complex parts produced. Even if the provider externally sources the simulation, his ability to understand and transform the simulation results into gating design demonstrates his competency level.
Core Making and Internal Geometry Control
Normally, the weakest component of the casting process is the core which is made of sand and is used to make internal cavities.
- Core Box Venting: The core binder gas needs an outlet. Improper venting results in the core getting blown, there will be a hole in the casting.
- Core Coating/Washing: In order for the metal not to seep into the cracks and stay smooth internally, the core is given a refractory coating.
- Core Setting: The application of chaplets (metallic props) to keep the core steady and not floating during the pour.
The 6% Benchmark: Quality Assurance and NDT
Industry standard in India is by a “raw casting” rejection rate of 3% to 6% which is typically consistent with the top-grade operations. Inordinate figures here would simply mean the controls mentioned above have broken down.
Non-Destructive Testing (NDT)
Far beneath what meets the eye, parts working hard in oil, gas, energy, or vehicle sectors need more than a quick look. That is why skilled sand casting makers in India carry:
- Cracks on the outside or just below show up through Magnetic Particle Inspection. This method spots flaws using tiny particles drawn by magnetic fields. Usually, it works when materials can hold magnetism well. Particles gather where breaks disrupt the flow underneath. Seen under proper light, these gatherings mark problem areas clearly.
- Peering inside parts? X-ray imaging spots trapped gases. Hidden voids show up clear. Shrinking during cooling leaves clues only radiography catches. Flaws beneath surfaces become visible through this method. What looks solid might hide pockets – this test reveals them.
- Inside thick metal parts, sound waves check wall depth plus hidden issues. A tool sends pulses through solid shapes to find thin spots along with internal breaks. Waves bounce back when they hit gaps inside poured materials. This method works deep within heavy sections where eyes cannot see. Signals show differences in material thickness together with problem areas.
Traceability and Documentation
In B2B engagements where professionalism prevails, every casting should have a heat number or date code marked on it. This makes it possible to analyze the situation where failure is found going back to the cause.
Assessing “Foundry 4.0” in the Indian Market
Globally, digitalization is influencing Indian foundries as well. Even though totally robot-operated foundries are a rarity, the “Smart Foundry” notion is gradually gaining acceptance especially in the realm of medium to major scale sand casting manufacturers of India.
- Continuous Sand Condition Checking: Installation of devices that track sand’s temperature and moisture changes at a 30-second interval.
- Energy Management: Considering that melting requires a lot of energy, utilization of smart meters helps to optimize power consumption which indirectly results in more stable melt cycles.
- Automated Pouring: Robots or semi-automated pouring ladles help significantly in the exact control of volume as well as speed of every batch pouring thus removal of human error from one of the most dangerous operations.
Summary of Actionable Advice for Buyers
- Agree on the tolerances before the stage: Do not conform to ‘standard’ sand casting tolerances only. State clearly how much precision you require e.g., Manufacturers applying automated high-pressure molding give this at an advantage of precision over manual hand-molding.
- Ask for the methoding plan: The gating and risering layout must accompany the order as this proves the manufacturer has thought about how the metal will solidify.
- Make pre-pour test mandatory: It is necessary that a contract states that a spectrometer check must be carried out before any metal is poured.
- Inspect the core shop: Most, if not all internal defects, are core related. Proper storage also is a must with a humidity-controlled and dry environment for cores.
- Don’t get fooled by just price: Low price normally indicates usage of cheaper sand additives, binders, or skipping Prerequisite Steps e.g. A cheap option in sand casting turns out to be more expensive after the metal rejection at the stage of machining is added.
Conclusion
Getting quotes from Sand Casting Manufacturers India embrace metallurgical tradition complemented by modern engineering. However, the responsibility for confirming is on the buyer’s side. Concentrating on the sand attributes, melt chemistry, and simulation-based design help an organization curtail casting process risks to a great extent.
The strongest collaborations formed in this industry are those that are based on technical honesty. When a manufacturer is able to show that they have strict control over the variables of sand, metal, and heat, they thereby become more than just a supplier. They are a link in the global value chain. If the buyer only knows what process controls to demand then the Indian market is ready for high-complexity, high-precision work.